Vector3 三维向量
结构体类型
表示 3D的 向量和点。
这个结构用于在 Unity 传递 3D 位置和方向。它包含向量运算的函数。
| 静态变量 | 值 |
|---|---|
| up | (0, 1, 0) |
| down | (0, -1, 0) |
| forward | (0, 0, 1) |
| back | (0, 0, -1) |
| left | (-1, 0, 0) |
| right | (1, 0, 0) |
| zero | (0, 0, 0) |
| one | (1, 1, 1) |
| 变量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| magnitude | 返回向量的长度(只读)。 |
| normalized | 返回该向量方向上的长度为1的向量(只读)。 |
| sqrMagnitude | 返回这个向量的长度的平方(只读)。 |
| this[int] | 使用[0], [1], [2]分别访问该向量的 x, y, z 元素。 |
| x | 向量的 x 元素 |
| y | 向量的 y 元素 |
| z | 向量的 z 元素 |
| 静态方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Angle | 返回两个向量之间的夹角。 |
| ClampMagnitude | 返回的向量的长度,最大不超过 maxLength 所指示的长度。 |
| Distance | 返回两个点之间的距离。 |
| Cross | 计算两个向量的叉乘。 |
| Dot | 计算两个向量的点乘。 |
| MoveTowards | 当前的地点移向目标。 |
| Max | 返回一个由两个向量的最大元素组成的向量。 |
| Min | 返回一个由两个向量的最小元素组成的向量。 |
| Lerp | 两个点之间的线性插值。 |
| LerpUnclamped | 两个向量之间的线性插值。该插值t在小于0或大于1时的返回值不会被限制。 |
| Normalize | 使向量的长度为1。 |
| Project | 投影一个向量到另一个向量。 |
| ProjectOnPlane | 投影向量到一个平面上(由垂直到该平面的法线定义)。 |
| Reflect | 沿着法线反射向量。 |
| SmoothDamp | 随着时间的推移,逐渐改变一个向量朝向预期的目标。 |
| RotateTowards | 当前的向量转向目标。 |
| OrthoNormalize | 使向量规范化并且彼此相互垂直。 |
| Scale | 两个矢量组件对应相乘。 |
| Slerp | 在两个向量之间球形插值。 |
| SlerpUnclamped | 在两个向量之间球形插值。该插值t在小于0或大于1时的返回值不会被限制。 |
Vector3.ClampMagnitude
返回原向量的拷贝,并且它的模最大不超过maxLength所指示的长度。 也就是说,限制向量长度到一个特定的长度。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Vector3 centerPt;
public float radius;
void Update() {
Vector3 movement = new Vector3(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), 0, Input.GetAxis("Vertical"));
Vector3 newPos = transform.position + movement;
Vector3 offset = newPos - centerPt;
transform.position = centerPt + Vector3.ClampMagnitude(offset, radius);
}
}
Vector3.Dot 点乘
两个向量的点乘积。 点积是一个浮点型的值,两个向量的长度相乘,然后乘以它们之间夹角的余弦值。 对于normalized向量,如果他们指向在完全相同的方向,Dot返回1。如果他们指向完全相反的方向,返回-1。对于其他的情况返回一个数(例如:如果是垂直的Dot返回0)。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform other;
void Update() {
if (other) {
Vector3 forward = transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.forward);
Vector3 toOther = other.position - transform.position;
if (Vector3.Dot(forward, toOther) < 0)
print("The other transform is behind me!");
}
}
}
Vector3.Cross 叉乘
两个向量的交叉乘积。 两个向量的叉积乘积结果在垂直于两个输入向量的三分之一个向量。结果的大小等于两个输入相乘,然后乘以输入向量之间的角度的正弦值。你可以确定的方向的结果向量使用“左手法则”。
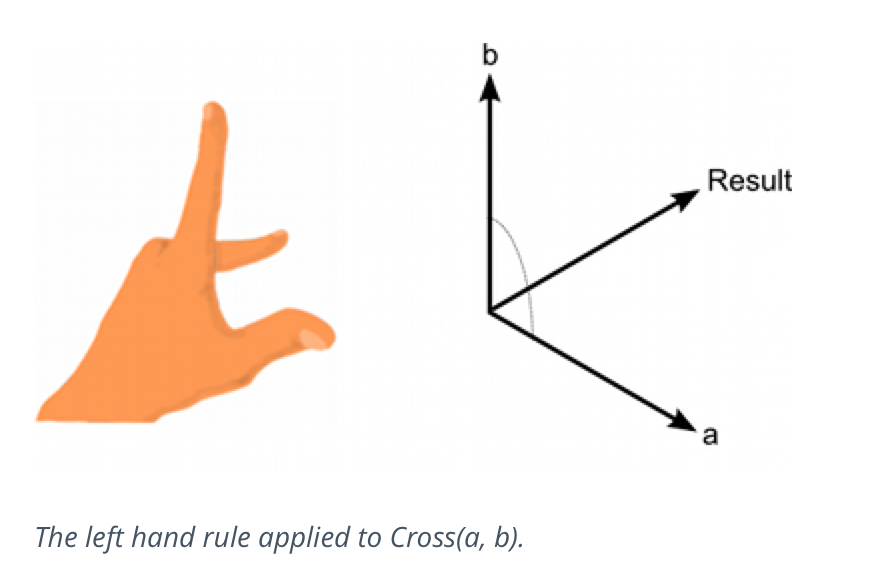 示例:
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
Vector3 GetNormal(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, Vector3 c) {
Vector3 side1 = b - a;
Vector3 side2 = c - a;
return Vector3.Cross(side1, side2).normalized;
}
}
Vector3.Lerp 线性差值
两个向量之间的线性插值。 按照分数t在from到to之间插值。这是最常用的寻找一点沿一条线的两个端点之间一些分数的方式(例如,在那些点之间逐渐移动一个对象)。这分数是在范围[ 0…1]。t是夹在 [0…1]之间,当t = 0时,返回from,当t = 1时,返回to。当t = 0.5 返回from和to的中间点。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform startMarker;
public Transform endMarker;
public float speed = 1.0F;
private float startTime;
private float journeyLength;
void Start() {
startTime = Time.time;
journeyLength = Vector3.Distance(startMarker.position, endMarker.position);
}
void Update() {
float distCovered = (Time.time - startTime) * speed;
float fracJourney = distCovered / journeyLength;
transform.position = Vector3.Lerp(startMarker.position, endMarker.position, fracJourney);
}
}
Vector3.Slerp 球形差值
两个向量之间的弧形插值 通过t数值在from和to之间插值。这与线性内插之间的不同(即, “线性插值” )是该向量被视为方向而不是空间中的点。返回的向量的方向是由角内插,其大小是from和to的幅度之间进行内插。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform sunrise;
public Transform sunset;
public float journeyTime = 1.0F;
private float startTime;
void Start() {
startTime = Time.time;
}
void Update() {
Vector3 center = (sunrise.position + sunset.position) * 0.5F;
center -= new Vector3(0, 1, 0);
Vector3 riseRelCenter = sunrise.position - center;
Vector3 setRelCenter = sunset.position - center;
float fracComplete = (Time.time - startTime) / journeyTime;
transform.position = Vector3.Slerp(riseRelCenter, setRelCenter, fracComplete);
transform.position += center;
}
}
Vector3.MoveTowards
当前的地点移向目标。 这个函数的返回值是一个点maxdistancedelta单位更接近于目标/点沿着当前的和目标之间的线。如果目标是比maxdistancedelta /然后返回值将等于目标接近(即移动不会超过目标)。maxdistancedelta负值可以用来从目标推开该向量。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform target;
public float speed;
void Update() {
float step = speed * Time.deltaTime;
transform.position = Vector3.MoveTowards(transform.position, target.position, step);
}
}
Vector3.SmoothDamp
随着时间的推移,逐渐改变一个向量朝向预期的目标。 向量由一些像弹簧阻尼器函数平滑,这将永远不会超过。最常见的用途是相机平滑跟随。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform target;
public float smoothTime = 0.3F;
private Vector3 velocity = Vector3.zero;
void Update() {
Vector3 targetPosition = target.TransformPoint(new Vector3(0, 5, -10));
transform.position = Vector3.SmoothDamp(transform.position, targetPosition, ref velocity, smoothTime);
}
}
Vector3.RotateTowards 转向
当前的向量转向目标。
这个函数类似于MoveTowards除了将向量被视为一个方向,而不是一个位置上。当前向量将被旋转朝向目标方向由maxRadiansDelta的角度,虽然会恰好落在目标,而不是超过。如果当前的大小和目标的是不同的,那么结果的幅度将被线性地旋转过程中进行插值。如果一个负值用于maxRadiansDelta ,向量会转离目标/直到它指向完全相反的方向,然后停止。
示例:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour {
public Transform target;
public float speed;
void Update() {
Vector3 targetDir = target.position - transform.position;
float step = speed * Time.deltaTime;
Vector3 newDir = Vector3.RotateTowards(transform.forward, targetDir, step, 0.0F);
Debug.DrawRay(transform.position, newDir, Color.red);
transform.rotation = Quaternion.LookRotation(newDir);
}
}
源码
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using scm = System.ComponentModel;
using uei = UnityEngine.Internal;
namespace UnityEngine
{
// Representation of 3D vectors and points.
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public partial struct Vector3
{
public const float kEpsilon = 0.00001F;
// X component of the vector.
public float x;
// Y component of the vector.
public float y;
// Z component of the vector.
public float z;
// Linearly interpolates between two vectors.
public static Vector3 Lerp(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, float t)
{
t = Mathf.Clamp01(t);
return new Vector3(
a.x + (b.x - a.x) * t,
a.y + (b.y - a.y) * t,
a.z + (b.z - a.z) * t
);
}
// Linearly interpolates between two vectors without clamping the interpolant
public static Vector3 LerpUnclamped(Vector3 a, Vector3 b, float t)
{
return new Vector3(
a.x + (b.x - a.x) * t,
a.y + (b.y - a.y) * t,
a.z + (b.z - a.z) * t
);
}
// Moves a point /current/ in a straight line towards a /target/ point.
public static Vector3 MoveTowards(Vector3 current, Vector3 target, float maxDistanceDelta)
{
Vector3 toVector = target - current;
float dist = toVector.magnitude;
if (dist <= maxDistanceDelta || dist < float.Epsilon)
return target;
return current + toVector / dist * maxDistanceDelta;
}
[uei.ExcludeFromDocs]
public static Vector3 SmoothDamp(Vector3 current, Vector3 target, ref Vector3 currentVelocity, float smoothTime, float maxSpeed)
{
float deltaTime = Time.deltaTime;
return SmoothDamp(current, target, ref currentVelocity, smoothTime, maxSpeed, deltaTime);
}
[uei.ExcludeFromDocs]
public static Vector3 SmoothDamp(Vector3 current, Vector3 target, ref Vector3 currentVelocity, float smoothTime)
{
float deltaTime = Time.deltaTime;
float maxSpeed = Mathf.Infinity;
return SmoothDamp(current, target, ref currentVelocity, smoothTime, maxSpeed, deltaTime);
}
// Gradually changes a vector towards a desired goal over time.
public static Vector3 SmoothDamp(Vector3 current, Vector3 target, ref Vector3 currentVelocity, float smoothTime, [uei.DefaultValue("Mathf.Infinity")] float maxSpeed, [uei.DefaultValue("Time.deltaTime")] float deltaTime)
{
smoothTime = Mathf.Max(0.0001F, smoothTime);
float omega = 2F / smoothTime;
float x = omega * deltaTime;
float exp = 1F / (1F + x + 0.48F * x * x + 0.235F * x * x * x);
Vector3 change = current - target;
Vector3 originalTo = target;
float maxChange = maxSpeed * smoothTime;
change = Vector3.ClampMagnitude(change, maxChange);
target = current - change;
Vector3 temp = (currentVelocity + omega * change) * deltaTime;
currentVelocity = (currentVelocity - omega * temp) * exp;
Vector3 output = target + (change + temp) * exp;
if (Vector3.Dot(originalTo - current, output - originalTo) > 0)
{
output = originalTo;
currentVelocity = (output - originalTo) / deltaTime;
}
return output;
}
// Access the x, y, z components using [0], [1], [2] respectively.
public float this[int index]
{
get
{
switch (index)
{
case 0: return x;
case 1: return y;
case 2: return z;
default:
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Invalid Vector3 index!");
}
}
set
{
switch (index)
{
case 0: x = value; break;
case 1: y = value; break;
case 2: z = value; break;
default:
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("Invalid Vector3 index!");
}
}
}
// Creates a new vector with given x, y, z components.
public Vector3(float x, float y, float z) { this.x = x; this.y = y; this.z = z; }
// Creates a new vector with given x, y components and sets /z/ to zero.
public Vector3(float x, float y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; z = 0F; }
// Set x, y and z components of an existing Vector3.
public void Set(float newX, float newY, float newZ) { x = newX; y = newY; z = newZ; }
// Multiplies two vectors component-wise.
public static Vector3 Scale(Vector3 a, Vector3 b) { return new Vector3(a.x * b.x, a.y * b.y, a.z * b.z); }
// Multiplies every component of this vector by the same component of /scale/.
public void Scale(Vector3 scale) { x *= scale.x; y *= scale.y; z *= scale.z; }
// Cross Product of two vectors.
public static Vector3 Cross(Vector3 lhs, Vector3 rhs)
{
return new Vector3(
lhs.y * rhs.z - lhs.z * rhs.y,
lhs.z * rhs.x - lhs.x * rhs.z,
lhs.x * rhs.y - lhs.y * rhs.x);
}
// used to allow Vector3s to be used as keys in hash tables
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return x.GetHashCode() ^ (y.GetHashCode() << 2) ^ (z.GetHashCode() >> 2);
}
// also required for being able to use Vector3s as keys in hash tables
public override bool Equals(object other)
{
if (!(other is Vector3)) return false;
Vector3 rhs = (Vector3)other;
return x.Equals(rhs.x) && y.Equals(rhs.y) && z.Equals(rhs.z);
}
// Reflects a vector off the plane defined by a normal.
public static Vector3 Reflect(Vector3 inDirection, Vector3 inNormal)
{
return -2F * Dot(inNormal, inDirection) * inNormal + inDirection;
}
// *undoc* --- we have normalized property now
public static Vector3 Normalize(Vector3 value)
{
float mag = Magnitude(value);
if (mag > kEpsilon)
return value / mag;
else
return zero;
}
// Makes this vector have a ::ref::magnitude of 1.
public void Normalize()
{
float mag = Magnitude(this);
if (mag > kEpsilon)
this = this / mag;
else
this = zero;
}
// Returns this vector with a ::ref::magnitude of 1 (RO).
public Vector3 normalized { get { return Vector3.Normalize(this); } }
// Dot Product of two vectors.
public static float Dot(Vector3 lhs, Vector3 rhs) { return lhs.x * rhs.x + lhs.y * rhs.y + lhs.z * rhs.z; }
// Projects a vector onto another vector.
public static Vector3 Project(Vector3 vector, Vector3 onNormal)
{
float sqrMag = Dot(onNormal, onNormal);
if (sqrMag < Mathf.Epsilon)
return zero;
else
return onNormal * Dot(vector, onNormal) / sqrMag;
}
// Projects a vector onto a plane defined by a normal orthogonal to the plane.
public static Vector3 ProjectOnPlane(Vector3 vector, Vector3 planeNormal)
{
return vector - Project(vector, planeNormal);
}
// Returns the angle in degrees between /from/ and /to/. This is always the smallest
public static float Angle(Vector3 from, Vector3 to)
{
return Mathf.Acos(Mathf.Clamp(Vector3.Dot(from.normalized, to.normalized), -1F, 1F)) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
// The smaller of the two possible angles between the two vectors is returned, therefore the result will never be greater than 180 degrees or smaller than -180 degrees.
// If you imagine the from and to vectors as lines on a piece of paper, both originating from the same point, then the /axis/ vector would point up out of the paper.
// The measured angle between the two vectors would be positive in a clockwise direction and negative in an anti-clockwise direction.
public static float SignedAngle(Vector3 from, Vector3 to, Vector3 axis)
{
Vector3 fromNorm = from.normalized, toNorm = to.normalized;
float unsignedAngle = Mathf.Acos(Mathf.Clamp(Vector3.Dot(fromNorm, toNorm), -1F, 1F)) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
float sign = Mathf.Sign(Vector3.Dot(axis, Vector3.Cross(fromNorm, toNorm)));
return unsignedAngle * sign;
}
// Returns the distance between /a/ and /b/.
public static float Distance(Vector3 a, Vector3 b)
{
Vector3 vec = new Vector3(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y, a.z - b.z);
return Mathf.Sqrt(vec.x * vec.x + vec.y * vec.y + vec.z * vec.z);
}
// Returns a copy of /vector/ with its magnitude clamped to /maxLength/.
public static Vector3 ClampMagnitude(Vector3 vector, float maxLength)
{
if (vector.sqrMagnitude > maxLength * maxLength)
return vector.normalized * maxLength;
return vector;
}
// *undoc* --- there's a property now
public static float Magnitude(Vector3 vector) { return Mathf.Sqrt(vector.x * vector.x + vector.y * vector.y + vector.z * vector.z); }
// Returns the length of this vector (RO).
public float magnitude { get { return Mathf.Sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z); } }
// *undoc* --- there's a property now
public static float SqrMagnitude(Vector3 vector) { return vector.x * vector.x + vector.y * vector.y + vector.z * vector.z; }
// Returns the squared length of this vector (RO).
public float sqrMagnitude { get { return x * x + y * y + z * z; } }
// Returns a vector that is made from the smallest components of two vectors.
public static Vector3 Min(Vector3 lhs, Vector3 rhs)
{
return new Vector3(Mathf.Min(lhs.x, rhs.x), Mathf.Min(lhs.y, rhs.y), Mathf.Min(lhs.z, rhs.z));
}
// Returns a vector that is made from the largest components of two vectors.
public static Vector3 Max(Vector3 lhs, Vector3 rhs)
{
return new Vector3(Mathf.Max(lhs.x, rhs.x), Mathf.Max(lhs.y, rhs.y), Mathf.Max(lhs.z, rhs.z));
}
static readonly Vector3 zeroVector = new Vector3(0F, 0F, 0F);
static readonly Vector3 oneVector = new Vector3(1F, 1F, 1F);
static readonly Vector3 upVector = new Vector3(0F, 1F, 0F);
static readonly Vector3 downVector = new Vector3(0F, -1F, 0F);
static readonly Vector3 leftVector = new Vector3(-1F, 0F, 0F);
static readonly Vector3 rightVector = new Vector3(1F, 0F, 0F);
static readonly Vector3 forwardVector = new Vector3(0F, 0F, 1F);
static readonly Vector3 backVector = new Vector3(0F, 0F, -1F);
static readonly Vector3 positiveInfinityVector = new Vector3(float.PositiveInfinity, float.PositiveInfinity, float.PositiveInfinity);
static readonly Vector3 negativeInfinityVector = new Vector3(float.NegativeInfinity, float.NegativeInfinity, float.NegativeInfinity);
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(0, 0, 0)@@
public static Vector3 zero { get { return zeroVector; } }
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(1, 1, 1)@@
public static Vector3 one { get { return oneVector; } }
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(0, 0, 1)@@
public static Vector3 forward { get { return forwardVector; } }
public static Vector3 back { get { return backVector; } }
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(0, 1, 0)@@
public static Vector3 up { get { return upVector; } }
public static Vector3 down { get { return downVector; } }
public static Vector3 left { get { return leftVector; } }
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(1, 0, 0)@@
public static Vector3 right { get { return rightVector; } }
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(float.PositiveInfinity, float.PositiveInfinity, float.PositiveInfinity)@@
public static Vector3 positiveInfinity { get { return positiveInfinityVector; } }
// Shorthand for writing @@Vector3(float.NegativeInfinity, float.NegativeInfinity, float.NegativeInfinity)@@
public static Vector3 negativeInfinity { get { return negativeInfinityVector; } }
// Adds two vectors.
public static Vector3 operator+(Vector3 a, Vector3 b) { return new Vector3(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y, a.z + b.z); }
// Subtracts one vector from another.
public static Vector3 operator-(Vector3 a, Vector3 b) { return new Vector3(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y, a.z - b.z); }
// Negates a vector.
public static Vector3 operator-(Vector3 a) { return new Vector3(-a.x, -a.y, -a.z); }
// Multiplies a vector by a number.
public static Vector3 operator*(Vector3 a, float d) { return new Vector3(a.x * d, a.y * d, a.z * d); }
// Multiplies a vector by a number.
public static Vector3 operator*(float d, Vector3 a) { return new Vector3(a.x * d, a.y * d, a.z * d); }
// Divides a vector by a number.
public static Vector3 operator/(Vector3 a, float d) { return new Vector3(a.x / d, a.y / d, a.z / d); }
// Returns true if the vectors are equal.
public static bool operator==(Vector3 lhs, Vector3 rhs)
{
// Returns false in the presence of NaN values.
return SqrMagnitude(lhs - rhs) < kEpsilon * kEpsilon;
}
// Returns true if vectors are different.
public static bool operator!=(Vector3 lhs, Vector3 rhs)
{
// Returns true in the presence of NaN values.
return !(lhs == rhs);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return UnityString.Format("({0:F1}, {1:F1}, {2:F1})", x, y, z);
}
public string ToString(string format)
{
return UnityString.Format("({0}, {1}, {2})", x.ToString(format), y.ToString(format), z.ToString(format));
}
[System.Obsolete("Use Vector3.forward instead.")]
public static Vector3 fwd { get { return new Vector3(0F, 0F, 1F); } }
[System.Obsolete("Use Vector3.Angle instead. AngleBetween uses radians instead of degrees and was deprecated for this reason")]
public static float AngleBetween(Vector3 from, Vector3 to) { return Mathf.Acos(Mathf.Clamp(Vector3.Dot(from.normalized, to.normalized), -1F, 1F)); }
[System.Obsolete("Use Vector3.ProjectOnPlane instead.")]
public static Vector3 Exclude(Vector3 excludeThis, Vector3 fromThat) { return ProjectOnPlane(fromThat, excludeThis); }
}
}
🔚